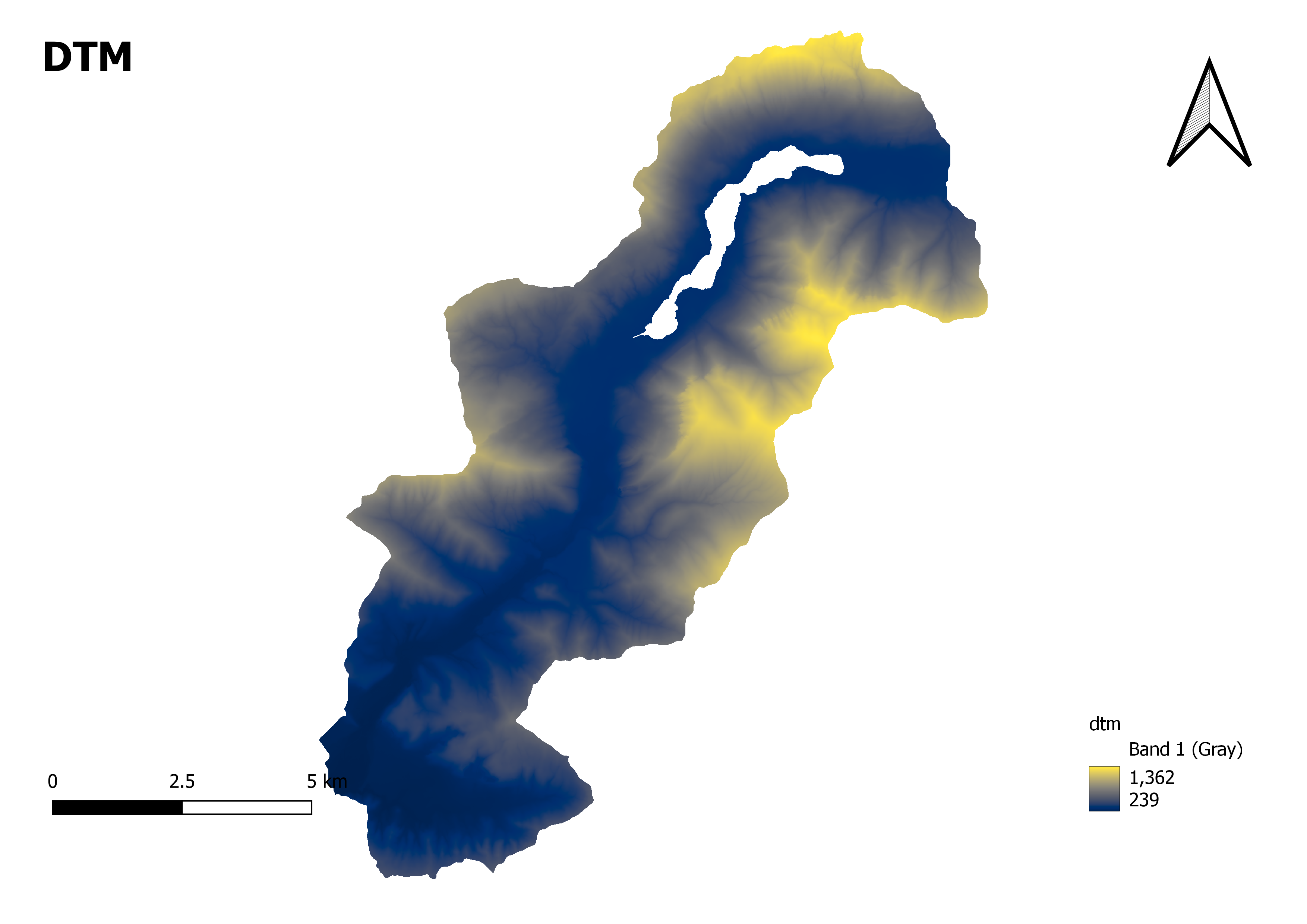
Digital Terrain Models
"DTM" stands for Digital Terrain Model. It is a digital representation of the Earth's surface, specifically focused on the elevation or topography of a particular area.
A DTM provides information about the height, slope, and shape of the terrain, allowing for accurate representation and analysis of the landscape. Satellite images, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) data, aerial pictures, and survey measurements are only some common ways a DTM is created.
Here's how you can interpret the elevation range in a DTM map:
Lower Values: The minimum value (in this case, 239) represents the lowest point or elevation within the mapped area. It could indicate areas such as valleys, depressions, or low-lying terrain.
Higher Values: The maximum value (in this case, 1362) represents the highest point or elevation within the mapped area. It could indicate mountain peaks, ridges, or elevated regions.
Elevation Range: The difference between the maximum and minimum values (1362 - 239 = 1123) represents the broad elevation range. This range suggests the extent of elevation differences within the mapped area.Understanding the range of elevation in a DTM map is crucial for various applications. It helps identify areas of steep slopes, prominent landforms, drainage patterns, or areas susceptible to flooding or erosion.