Aspect Exploratory data analysis
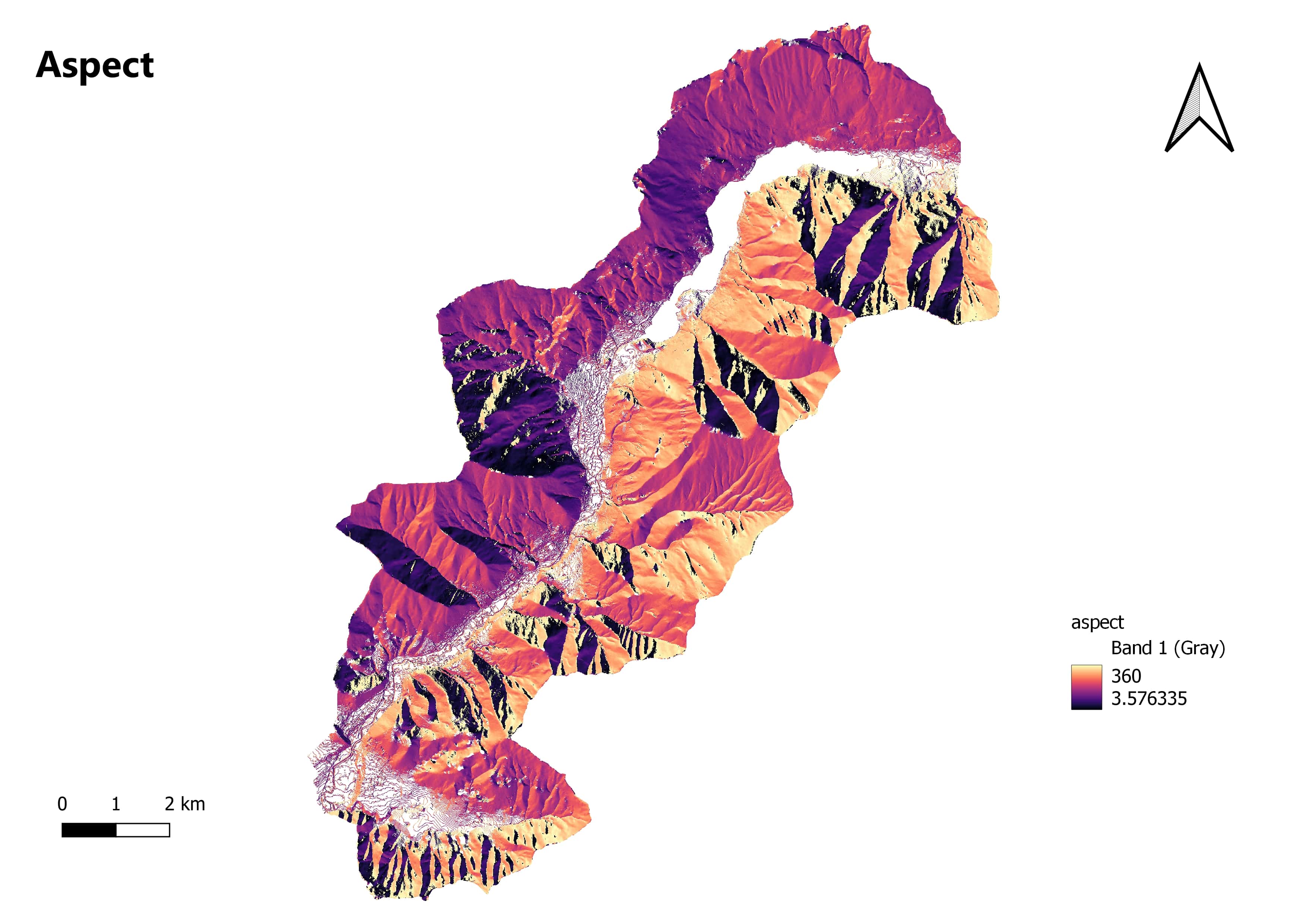
"Aspect" refers to a specific terrain or topographic attribute of a geographic landscape. It represents the direction that a slope or a land surface faces, typically measured in degrees clockwise from north.
Aspect in QGIS can be calculated for a digital elevation model (DEM) or a raster dataset representing elevation values. DEMs are commonly derived from elevation data captured by satellites, airborne sensors, or ground surveys. QGIS provides various tools and functionalities to analyze and visualize aspect information.
Aspect Calculation: QGIS provides tools to calculate aspect values from Digital Elevation Models (DEMs). The "Aspect" tool generates an output raster with aspect values for each pixel in the DEM. Aspect values range from 0 to 360 degrees, representing different directions (0 degrees for north, 90 degrees for east, 180 degrees for south, and 270 degrees for west).
Aspect Visualization: QGIS allows you to visualize aspect data in various ways. You can apply color ramps or gradient styles to represent aspect values, creating visually appealing hillshade maps that highlight slope directions. By adjusting the light source, you can control shading and emphasize specific aspects.
Aspect Analysis: Aspect information is useful for different GIS analyses. For example, it can help identify slopes facing a specific direction, such as north-facing slopes, which can have implications for vegetation distribution, solar radiation exposure, or hydrological processes. Aspect can also be combined with other terrain attributes like slope or elevation to derive additional information or perform further analysis.
Terrain and Landscape Analysis: Aspect is often used in combination with other terrain attributes to gain insights into the landscape. For instance, combining aspect and slope data can help identify different landforms like ridges, valleys, or flat areas. Aspect analysis is also valuable for site selection, viewshed analysis, or studying the influence of topography on various phenomena.
Aspect-Based Mapping: Aspect information can be utilized to create specialized maps for specific applications. In agriculture, aspect maps can help determine suitable areas for crop cultivation based on solar exposure and temperature variation. In urban planning, aspect analysis aids in understanding shading patterns and the solar potential of different areas.